Chemical reactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, involving the transformation of one or more substances into new substances. At the heart of every chemical reaction are reactants and products. Reactants are the substances that undergo a chemical change to form new substances, known as products. The relationship between reactants and products is a crucial aspect of understanding chemical reactions, as it helps chemists predict and analyze the outcomes of various chemical processes.
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products. This principle is essential in balancing chemical equations, which is a critical step in understanding the stoichiometry of chemical reactions. The stoichiometry of a reaction refers to the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products, and it is expressed through the use of coefficients in a balanced chemical equation.
A thorough understanding of reactants and products is vital in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. In chemistry, the study of reactants and products helps in the development of new materials, pharmaceuticals, and fuels. In biology, the understanding of biochemical reactions, where reactants are converted into products through enzyme-catalyzed reactions, is crucial for comprehending metabolic pathways and the functioning of living organisms. Environmental science also relies on the knowledge of reactants and products to assess and mitigate the impact of pollution and to develop sustainable practices.
Key Points
- Reactants are the substances that undergo chemical change to form new substances called products.
- The law of conservation of mass dictates that the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products in a chemical reaction.
- Understanding the relationship between reactants and products is crucial for predicting and analyzing chemical reactions.
- The stoichiometry of a reaction, expressed through balanced chemical equations, provides a quantitative relationship between reactants and products.
- Knowledge of reactants and products is essential in fields like chemistry, biology, and environmental science for various applications and research.
Reactants in Chemical Reactions
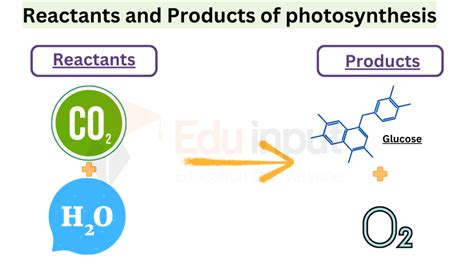
Reactants are the starting materials in a chemical reaction. They can be elements or compounds and are typically shown on the left side of a chemical equation. The nature and amount of reactants used in a reaction can significantly influence the outcome, including the yield and purity of the products. Reactants can undergo various types of chemical changes, such as combustion, synthesis, decomposition, or replacement reactions, depending on the conditions and the other reactants involved.
One of the critical aspects of reactants is their reactivity, which is influenced by factors such as their chemical structure, the presence of catalysts, temperature, and pressure. Understanding the reactivity of different substances is essential for designing and optimizing chemical reactions. Moreover, the selection of appropriate reactants is crucial for achieving specific products with desired properties, which is a key challenge in synthetic chemistry.
Types of Reactants
Reactants can be broadly classified into several types based on their chemical properties and the roles they play in reactions. For instance, limiting reactants are those that are completely consumed during a reaction and determine the maximum amount of product that can be formed. Excess reactants, on the other hand, are those that are present in quantities greater than needed to react with the limiting reactant, ensuring that the reaction proceeds to completion.
Catalysts are another type of reactant that speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, thereby increasing the reaction rate. Catalysts are crucial in many industrial processes and biological systems, enabling reactions to proceed efficiently under mild conditions.
| Type of Reactant | Description |
|---|---|
| Limiting Reactant | The reactant that is completely consumed and determines the maximum amount of product formed. |
| Excess Reactant | The reactant present in quantities greater than needed to react with the limiting reactant. |
| Catalyst | A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed. |

Products in Chemical Reactions
Products are the substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction. They are shown on the right side of a chemical equation and can be elements, compounds, or a mixture of both. The formation of products is a direct consequence of the chemical changes undergone by the reactants. Understanding the nature and properties of products is essential for various applications, including the synthesis of new materials, the development of pharmaceuticals, and the assessment of environmental impact.
The yield and purity of products are critical factors in chemical synthesis. The yield refers to the amount of product obtained from a reaction, usually expressed as a percentage of the theoretical maximum yield. Maximizing yield while minimizing impurities is a key challenge in chemical synthesis, requiring careful control of reaction conditions and the selection of appropriate reactants and catalysts.
Characterization of Products
The characterization of products involves determining their chemical structure, physical properties, and purity. Various analytical techniques, such as spectroscopy (IR, NMR, MS), chromatography (GC, HPLC), and X-ray diffraction, are used to identify and characterize the products of a chemical reaction. These techniques provide invaluable information about the molecular structure, composition, and properties of the products, which is essential for understanding their reactivity, stability, and potential applications.
The characterization of products also plays a critical role in quality control, especially in the production of pharmaceuticals and food additives, where the purity and identity of the products must meet strict regulatory standards. Moreover, in environmental science, the characterization of products from chemical reactions can help in understanding and mitigating the impact of pollutants on ecosystems.
What is the significance of understanding reactants and products in chemical reactions?
+Understanding reactants and products is crucial for predicting and analyzing chemical reactions, which is vital for various applications in chemistry, biology, and environmental science. It helps in designing efficient reactions, synthesizing new materials, and assessing environmental impact.
How do catalysts influence chemical reactions?
+Catalysts speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They are not consumed in the process and can significantly influence the rate and efficiency of reactions, making them crucial in industrial processes and biological systems.
What is the importance of characterizing products in chemical reactions?
+Characterizing products is essential for determining their chemical structure, physical properties, and purity. This information is vital for understanding their reactivity, stability, and potential applications, as well as for quality control in the production of substances like pharmaceuticals and food additives.
In conclusion, the study of reactants and products in chemical reactions is fundamental to understanding the principles of chemistry and applying them in various fields. By grasping the concepts of reactants, products, and their interrelationships, scientists and researchers can develop new materials, design more efficient processes, and contribute to sustainable development. As our understanding of chemical reactions evolves, so does our ability to innovate and address the complex challenges facing our world today.
