The reporting of GPA scales has become an essential aspect of academic evaluation, providing a standardized measure of student performance across various institutions. The GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a numerical representation of a student's academic achievement, calculated based on the grades earned in their coursework. With the increasing importance of academic records in college admissions, career opportunities, and academic research, the accurate reporting of GPA scales has become a critical concern for educational institutions, students, and employers alike.
Understanding GPA Scales
GPA scales are typically based on a 4.0 scale, with letter grades (A, B, C, D, and F) assigned to students based on their performance in a particular course. Each letter grade corresponds to a specific grade point value, ranging from 0 to 4.0. The GPA is then calculated by averaging the grade points earned in all courses completed by a student. However, the reporting of GPA scales can vary significantly between institutions, with some using a weighted GPA scale, which assigns more weight to advanced or honors courses, while others use an unweighted scale.
GPA Scale Variations
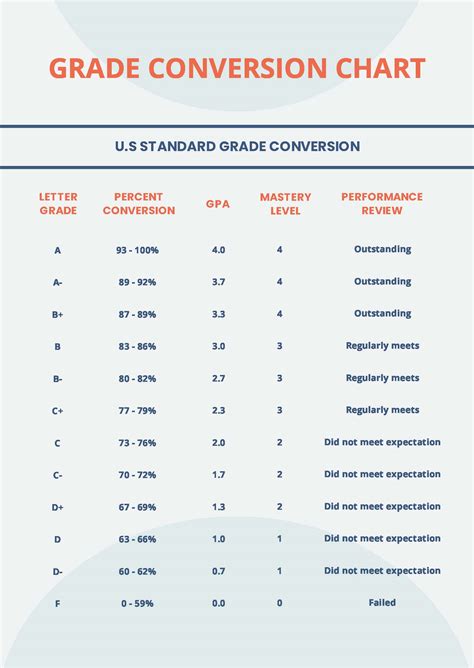
One of the primary challenges in reporting GPA scales is the variation in scales used by different institutions. Some colleges and universities use a 4.3 or 4.5 scale, which allows for more nuanced differentiation between students. Additionally, some institutions may use a plus/minus grading system, which can further complicate the calculation of GPA. For instance, a grade of A- may be assigned a grade point value of 3.7, while an A+ may be assigned a value of 4.3. Understanding these variations is essential for accurate reporting and comparison of GPAs across institutions.
| GPA Scale | Grade Point Value |
|---|---|
| A | 4.0 |
| A- | 3.7 |
| B+ | 3.3 |
| B | 3.0 |
| B- | 2.7 |
| C+ | 2.3 |
| C | 2.0 |
| C- | 1.7 |
| D+ | 1.3 |
| D | 1.0 |
| D- | 0.7 |
| F | 0.0 |
Key Points
- The reporting of GPA scales is crucial for academic evaluation and comparison.
- GPA scales can vary between institutions, with some using weighted or unweighted scales.
- Understanding the specific GPA scale used by an institution is essential for accurate reporting and comparison.
- Plus/minus grading systems can further complicate GPA calculations.
- Consideration of grading policies and procedures is necessary for accurate evaluation of GPAs.
Implications of GPA Scale Reporting

The accurate reporting of GPA scales has significant implications for students, educational institutions, and employers. For students, a accurately reported GPA can impact college admissions, scholarship eligibility, and future career opportunities. For institutions, accurate GPA reporting is essential for evaluating student performance, identifying areas for improvement, and maintaining academic integrity. Employers also rely on GPA reports to assess a candidate’s academic achievement and potential for success in the workplace.
Best Practices for GPA Scale Reporting
To ensure accurate and consistent reporting of GPA scales, educational institutions should establish clear policies and procedures for calculating and reporting GPAs. This includes providing transparent information about the GPA scale used, as well as any variations in grading policies or procedures. Additionally, institutions should ensure that GPA reports are accurate, complete, and easily accessible to students, employers, and other authorized parties.
What is the most commonly used GPA scale?
+The most commonly used GPA scale is the 4.0 scale, with letter grades (A, B, C, D, and F) assigned to students based on their performance in a particular course.
How do plus/minus grading systems affect GPA calculations?
+Plus/minus grading systems can further complicate GPA calculations, as they assign more nuanced grade point values to students. For example, an A- may be assigned a grade point value of 3.7, while an A+ may be assigned a value of 4.3.
Why is accurate GPA scale reporting important?
+Accurate GPA scale reporting is essential for evaluating student performance, identifying areas for improvement, and maintaining academic integrity. It also impacts college admissions, scholarship eligibility, and future career opportunities.
In conclusion, the reporting of GPA scales is a critical aspect of academic evaluation, with significant implications for students, educational institutions, and employers. By understanding the variations in GPA scales, institutions can ensure accurate and consistent reporting, providing a more nuanced representation of student achievement. As the importance of academic records continues to grow, the accurate reporting of GPA scales will remain a vital concern for all stakeholders involved.
